Options Abound To Suit Your
Cultivation Goals
Traditional Greenhouses
Completely enclosed buildings with a controlled climate for continuous year-round growing of a variety of crops.

Poly tunnel greenhouses
Economical, partially enclosed buildings that lengthen the growing season while protecting from inclement weather.

Shade Houses
Shade Houses, strategically designed for partial shade, provide an ideal environment for cultivating outdoor plants and shade-loving varieties, fostering optimal growth in protected conditions.
Aquaponics and hydroponics
These are high-tech systems that combine gardening with fish farming or nutrient-rich water solutions for sustainable food production.
Sustainability Sprouts For A Greener Tomorrow
- Year-round Cultivation
- Enhanced Crop Quality
- Resource Efficiency
- Sustainable Agriculture
-

Elevate Agriculture With Year-Round Cultivation Practices
Regardless of seasonal variations, greenhouse farming enables the year-round cultivation of crops. The ideal circumstances for plant growth can be maintained in greenhouses by offering a controlled atmosphere. By extending the growing season, a more consistent and predictable food supply is ensured, which lessens the vulnerability to climatic interruptions. Improved food security is a result of farmers' ability to diversify their crops and satisfy market demands even during the off-season.
-
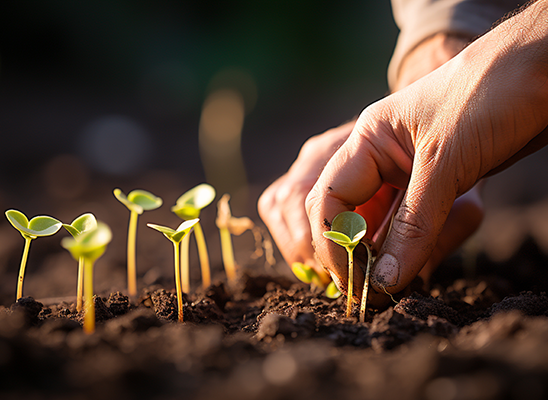

Maximizing Crop Quality Through Innovation
The greenhouse's regulated atmosphere makes it possible to precisely control variables like temperature, humidity, and light exposure. Increased yields and greater crop quality are the outcomes of this control. Less pressure from pests and diseases allows plants to develop, producing healthier and more marketable products. The taste, look, and nutritional content of fruits and vegetables grown in greenhouses are frequently improved, answering consumer demands for premium, regionally sourced produce.
-
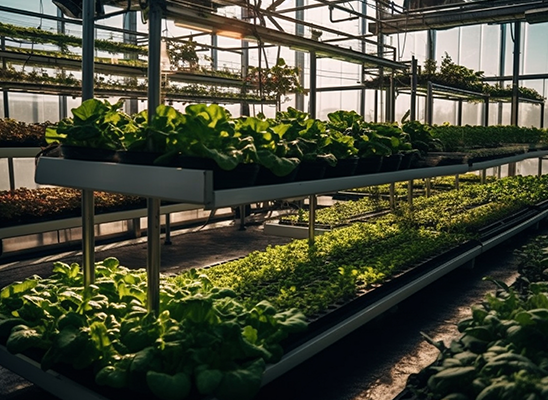

A Pathway ToMinimize Waste, Maximize Impact
Greenhouses are created with resource efficiency in mind. Because water can be recycled and managed inside the enclosed environment, they consume less water than conventional open-field farming. Additionally, the controlled climate minimizes environmental implications by reducing the need for excessive pesticide and fertilizer treatments. Resource-saving techniques not only assist the environment but also help farmers cut costs..
-

Balancing Growth And Ecology
Greenhouse farming adheres to sustainability standards. It reduces waste and environmental harm by giving crops a protected, regulated environment. A decreased carbon footprint is also a result of shorter fresh product transportation routes. Furthermore, greenhouse farming can incorporate environmentally and socially responsible agricultural methods like organic farming, integrated pest management, and soil health enhancement.
-

Gated Community Farms
-
High Value trees
-

Water Management
-
Proper Electricity Connection
-

Man Power Support
The Art Of Design: Shapes For Successful Greenhouse Farming
Growing plants in greenhouses allows for freedom in both what you plant and how you set up your panting space.

Quonset or Hoop Houses

Gable Roof Greenhouses

Lean-to or Attached Greenhouses
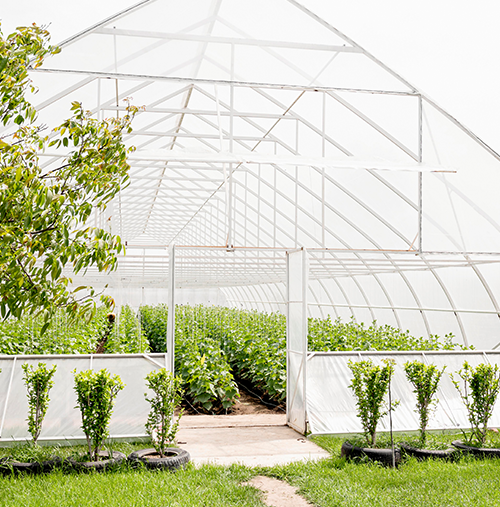

Quonset greenhouses are made of plastic or polyethylene film and have a semicircular or hoop-shaped frame. Hoop houses have the benefits of being affordable and simple to put together. They are good for prolonging the growing season and shielding crops from bad weather because they offer great light diffusion. Perfect for use in high-tunnel and seasonal applications.
Greenhouses with a gable roof typically feature a peaked roof. Typically, they have wooden or metal frames with glass or polycarbonate panels on top. Gable roof greenhouses have the benefit of a roomier interior and a more vertical area. They are suitable for the year-round production of a range of crops due to their design, which improves air circulation and provides better control over temperature and humidity.
Attached to an existing structure, such as a house or a building, lean-to greenhouses are greenhouses. They come in a variety of designs and frequently feature a roof with a single slope. Lean-to greenhouses utilize the available space well and can utilize the adjacent building's heating and cooling systems. They give simple access to the greenhouse from the attached building and are perfect for growers with limited space.
Where seeds of income flourish into a bountiful harveste
In addition to providing sustainable and managed food production, greenhouse farming offers a variety of income prospects. Beyond crop sales, greenhouse farmers can explore niche markets with specialty crops, add value to their harvest through processing into products like jams or skincare items, and offer farm-to-table experiences or CSA programs. They can also generate revenue through agritourism, hosting educational workshops, farm tours, and events that promote sustainable agriculture. These diverse income streams not only contribute to the financial success of greenhouse farming but also support local communities and foster a deeper appreciation for sustainable food systems. Furthermore, greenhouse farming opens avenues for revenue generation by cultivating high-value specialty crops like microgreens or exotic herbs, which appeal to niche markets and command premium prices. Value-added products such as preserves, sauces, or dried herbs can significantly enhance profitability.
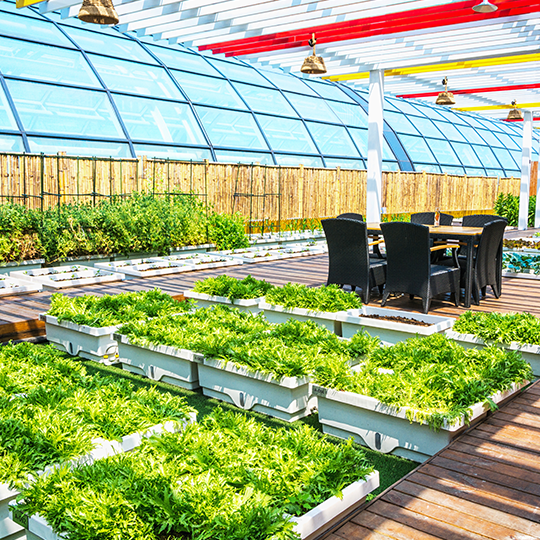


Crop Sales
You can raise high-quality, premium crops in greenhouses that you can then sell directly to customers, eateries, or regional marketplaces.
Sales of seedlings and nursery stock
Make use of your greenhouse to grow seedlings and nursery stock for other farmers, gardeners, and landscaping companies.

Activities for Education and Agritourism
Greenhouse farms present a special chance for educational and agritourism activities. You can hold workshops, lead tours, or even on-site classes to educate about greenhouse farming
Discover Solutions with Ease in Our
Comprehensive FAQ Collection
-
What is greenhouse farming, and how does it work?
Greenhouse farming involves the cultivation of crops within a controlled environment. Greenhouses use technology to regulate temperature, humidity, and other factors to create ideal growing conditions.
-
What are the benefits of greenhouse farming compared to traditional open-field farming?
Greenhouse farming offers advantages such as year-round cultivation, enhanced crop quality, resource efficiency, and reduced environmental impact.
-
What types of crops can be grown in greenhouses?
Greenhouses can accommodate a wide range of crops, including vegetables, herbs, flowers, fruits, and even specialty or exotic plants.
-
How much does it cost to set up a greenhouse farm?
The cost of setting up a greenhouse farm varies widely depending on size, design, location, and technology. It can range from small, affordable structures to larger, high-tech facilities.
-
Do greenhouse farms require special training or expertise?
While not mandatory, knowing greenhouse management and horticulture practices can be highly beneficial for greenhouse farmers.

